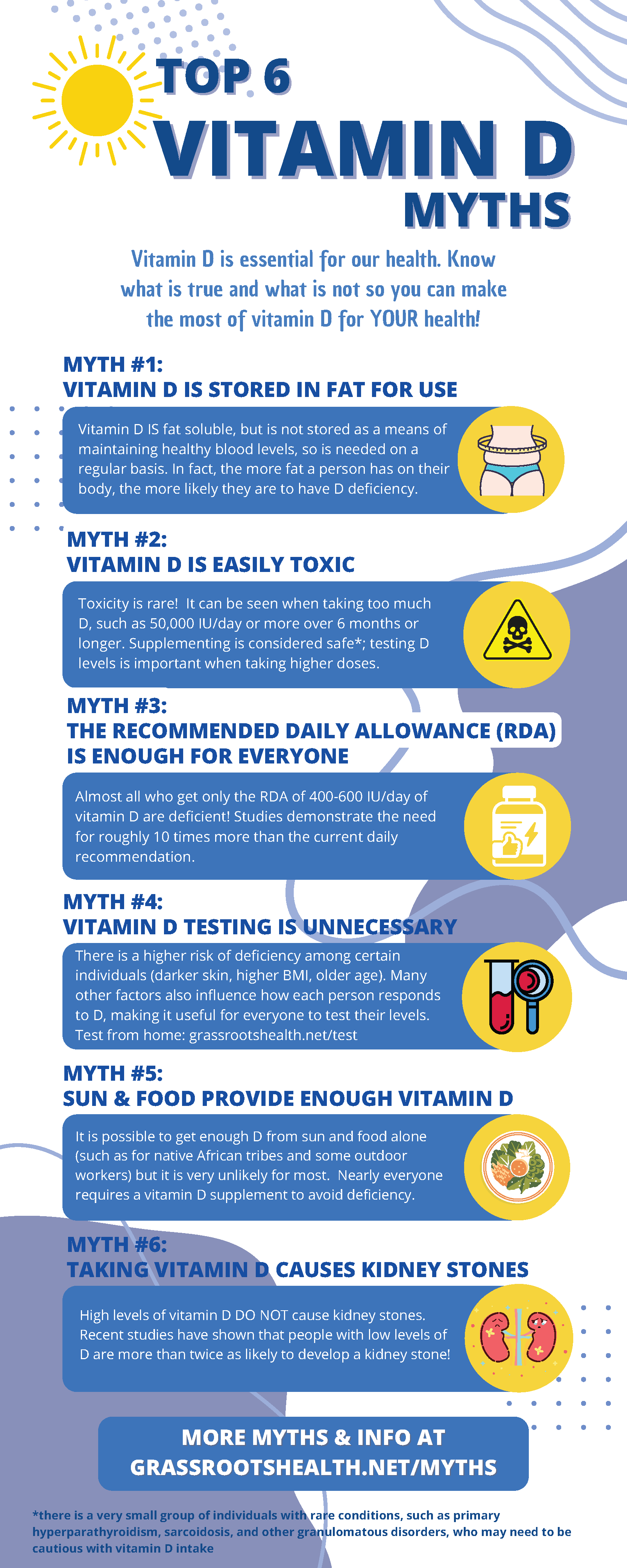
How Vitamin D Work In Human Body . supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. Few foods are naturally rich in. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it.
from www.grassrootshealth.net
Few foods are naturally rich in. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it.
Top 6 Vitamin D Myths Infographic GrassrootsHealth
How Vitamin D Work In Human Body The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. Few foods are naturally rich in. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much.
From www.dreamstime.com
When a VitaminD into Body. Stock Vector Illustration of anatomy How Vitamin D Work In Human Body learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. Few foods are naturally rich in. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From www.scribd.com
Lesson 8 Vitamin D and Health The Missing Vitamin in Humans pp.1 How Vitamin D Work In Human Body Few foods are naturally rich in. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From www.youtube.com
10 Signs Your Body Is Begging for Vitamin D YouTube How Vitamin D Work In Human Body vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal,. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From bestschoolnews.com
A Guide to Vitamins and Minerals for Beginners Best School News How Vitamin D Work In Human Body learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. Few. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From med.libretexts.org
9.5 Vitamin D Important to Bone Health and Beyond Medicine LibreTexts How Vitamin D Work In Human Body The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. Few foods are naturally rich in. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From www.dreamstime.com
Vitamin D Deficiency. Human Body, and Closeup of Organs with Effects How Vitamin D Work In Human Body vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. Few foods are. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From rmcskin.com
Vitamin D Benefits for Skin and Hair Rehman Medical Center How Vitamin D Work In Human Body Few foods are naturally rich in. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. The primary role of vitamin. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From www.pinterest.co.kr
Vitamins and minerals are important nutrients that play important roles How Vitamin D Work In Human Body supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From cheatdaydesign.com
Vitamin Cheat Sheet Visual Guide For All 13 Vitamins How Vitamin D Work In Human Body learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From mensmindgp.com
Why we need Vitamin D for mental health Dr Ed Rainbow How Vitamin D Work In Human Body The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health,. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From creehome.com
Best Normal Range Of Vitamin D In Human Body Cree Home How Vitamin D Work In Human Body vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From med.libretexts.org
10.2 Classification of Vitamins and Minerals Medicine LibreTexts How Vitamin D Work In Human Body Few foods are naturally rich in. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From 2012books.lardbucket.org
Micronutrients Essential for Bone Health Calcium and Vitamin D How Vitamin D Work In Human Body vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. Few foods are naturally rich in. The primary role. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From vectormine.com
Functions of vitamin D in human body and sources in food outline How Vitamin D Work In Human Body learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. Few foods are naturally rich in. vitamin d is essential for the bones. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From www.researchgate.net
Vitamin D and human skin. Vitamin D 3 is synthesized endogenously in How Vitamin D Work In Human Body The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. Few foods are naturally rich in. learn more about vitamin d and your health,. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From studyposter.blogspot.com
Ch 11 Case Study Low Serum Vitamin D Study Poster How Vitamin D Work In Human Body supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. The primary role of vitamin d is to ensure sufficient blood levels of calcium, and it. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From drjockers.com
How Vitamin D Stops Cancer Stem Cells How Vitamin D Work In Human Body Few foods are naturally rich in. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the immune system, brain health, and for regulating inflammation. supports bone health by increasing calcium levels. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. learn more about vitamin d. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.
From scriptlifepharmacy.com
Why All This Talk About Vitamin D3? Script Pharmacy How Vitamin D Work In Human Body learn more about vitamin d and your health, as well as what happens when you get too much and how much. Few foods are naturally rich in. vitamin d isn't naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, fortified cereal, and fatty. vitamin d is essential for the bones and teeth, the. How Vitamin D Work In Human Body.